Big Data and the cloud have a synergistic relationship that enables organizations to harness vast amounts of data efficiently and effectively. Here’s an overview of how cloud computing supports big data initiatives and the benefits of integrating the two:
Understanding Big Data
Big Data refers to the large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that inundate businesses daily. The characteristics of big data are often summarized by the “Three Vs”:
- Volume: The sheer amount of data generated and stored.
- Velocity: The speed at which data is created, processed, and analyzed.
- Variety: The different types of data (text, images, videos, etc.) coming from various sources.
The Role of Cloud Computing in Big Data
- Scalability
- Elastic Resources: Cloud platforms allow organizations to scale their resources up or down based on data processing needs, ensuring they can handle large datasets without investing in physical infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency
- Pay-as-You-Go Model: Organizations can pay only for the resources they use, reducing costs associated with maintaining on-premises hardware and software.
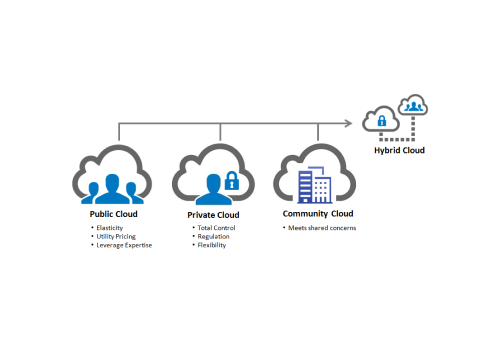
- Data Storage and Management
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Services like Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, and Azure Blob Storage provide scalable storage options for storing vast amounts of data reliably and securely.
- Processing Power
- Distributed Computing: Cloud providers offer powerful processing capabilities, enabling the use of frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark for distributed data processing across multiple nodes.
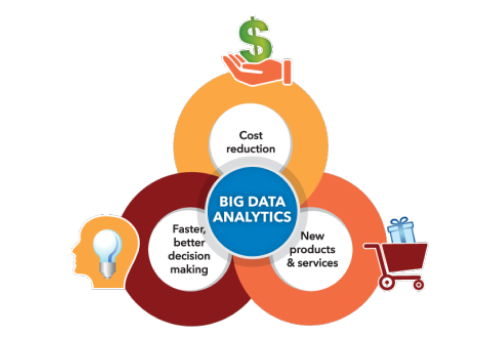
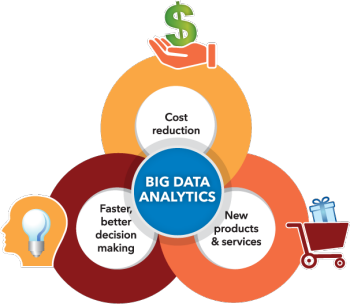
- Data Analytics and Insights
- Integrated Tools: Cloud platforms often come with built-in analytics tools (e.g., Azure Synapse, Google BigQuery) that allow organizations to analyze data quickly and derive insights without complex setup.
- Real-Time Data Processing
- Stream Processing Services: Cloud solutions like Azure Stream Analytics and AWS Kinesis enable real-time data ingestion and processing, allowing organizations to respond to data as it flows in.
- Collaboration and Accessibility
- Global Access: Cloud-based solutions facilitate collaboration by allowing teams to access and analyze data from anywhere, promoting a more agile and responsive approach to data management.
- Security and Compliance
- Advanced Security Measures: Cloud providers invest heavily in security technologies and compliance frameworks, offering features like encryption, access controls, and auditing to protect sensitive data.
Use Cases of Big Data in the Cloud
- Customer Insights: Organizations can analyze large datasets from customer interactions to understand preferences, optimize marketing strategies, and enhance customer experiences.
- Predictive Analytics: Companies can use historical data to forecast future trends, improve inventory management, and make data-driven decisions.
- IoT Data Management: The cloud provides the infrastructure necessary to store and process data generated from Internet of Things (IoT) devices, enabling real-time analysis and insights.
- Social Media Analytics: Businesses can leverage big data analytics to monitor social media trends, sentiment analysis, and engagement metrics to inform marketing strategies.
Conclusion
The combination of big data and cloud computing offers organizations the flexibility, scalability, and power needed to manage and analyze vast amounts of data effectively. By leveraging cloud-based tools and services, businesses can unlock valuable insights, enhance decision-making, and drive innovation, all while minimizing costs and complexity. Embracing this synergy is essential for any organization looking to thrive in today’s data-driven landscape.